Transoral Gastroplasty is the new type of weight loss surgery that has hit the bariatric world.
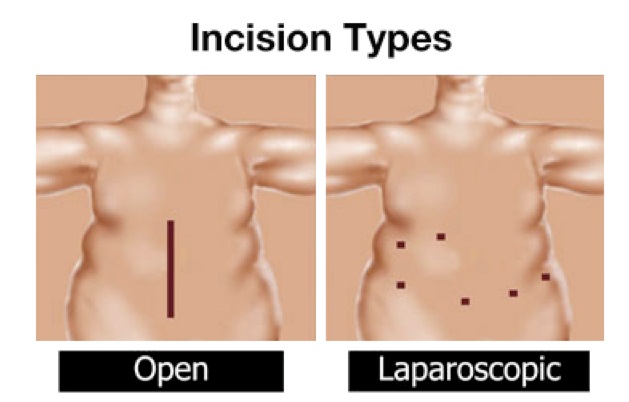
This surgery allows doctors to use a tool to go in through the patient’s mouth instead of cutting into their abdomen laparoscopically to complete the procedure.
This leads to no abdominal scars, faster recovery time, and less chance of infection.
TOGA is similar to vertical banded gastroplasty bariatric surgery.
The instrument is placed down the patient’s relaxed and open mouth and throat while they are under anesthesia.
A small camera is attached to the end of the tool in order for the doctor to see what they are doing during the bariatric surgery.
The tool expands once it is at the opening of the stomach to begin the procedure.
A small part of the stomach is stapled off from the rest, thereby letting food slowly drop down to the rest of the stomach to begin the digestive process.
None of the small intestines or other organs are changed as it is with gastric bypass weight loss surgery.
Even though this surgery is still largely experimental, experts estimate that it will be ready for clinical use as early as 2010.
Additionally, because this surgery is so new, doctors are unsure of the long and short term effects, such as amount of weight loss and how long it is kept off.
Any negative effects are also not immediately known, except for throat soreness after surgery.
Currently two companies have developed medical devices for the transoral gastroplasty surgery. The TOGA (Transoral Gastroplasty) tool was developed by Satiety, Inc. and is currently under medical trials for approval by the FDA.
During medical trials, test patients undergo the surgery and then they are followed for twelve months afterward to track their weight loss, side effects, and overall results.
Test patients are volunteers and are not required to pay for their weight loss surgery. TOGA is currently the other product that Satiety, Inc. has introduced to the public for testing.
The other company, USGI Medical, has developed the Primary Obesity Surgery Endoscopic (POSE) tool, which serves the same basic purpose and results as the TOGA instrument. It has also undergone clinical trials and has shown promising results.
Besides developing POSE, USGI Medical also has tools that reduce pouch or stoma sizes in gastric bypass patients who have stretched their pouch to the extent that they are now re-gaining their lost weight back.
This technology is also new to the bariatric surgery market.
Both USGI Medical and Satiety, Inc. are companies solely focused on developing incisionless surgery techniques and instruments.
The estimated cost of the procedure once it is made available to the public is not immediately known.